- Remittance
- Exchange Rate
- Stock
- Events
- EasyCard
- More
- Download
- Creator

What are the differences between SWIFT, IBAN, ABA, ACH, and BSB numbers mentioned during cross-borde
When conducting international/cross-border remittances, you may encounter the need to fill in SWIFT codes or other codes. Many friends may not be able to distinguish the differences between these common codes and why they need to be filled in.
This is because different countries and regions follow different transaction systems, so when transferring money to different parts of the world, a designated identification code is required. This number is equivalent to the ID number of each bank and is a type of bank code required for cross-border remittance. During telegraphic transfer, the remitter sends a payment message according to the international telegraphic transfer code of the receiving bank, and the payment can be transferred to the receiving bank.
For example, IBAN is required for remittance to Europe, ABA Number is required for remittance to US…
Today, let’s talk about the four common codes in cross-border remittance, hoping to be helpful to everyone!
International Code SWIFT Code
The SWIFT Code is a bank identification code proposed by the SWIFT Association and approved by ISO. Each member bank of the association has its own specific SWIFT code. During telegraphic transfer, the remitter sends a payment message according to the SWIFT CODE of the receiving bank, and the payment can be remitted to the receiving bank. This number is equivalent to the ID number of each bank, and its original name is BIC (Bank Identifier Code).
Each bank applying to join the SWIFT organization must first establish its own SWIFT address code in accordance with the unified principles of the SWIFT organization, which will take effect after approval by the SWIFT organization. During telegraphic transfer, the remittance agent sends a payment telegram according to the SWIFT Code of the receiving bank to transfer the funds to the receiving bank, which is equivalent to the ID number of each bank.
SWIFT codes are composed of 8 or 11 characters and can be divided into 4 parts to identify banking institutions, countries, locations, and branches.
The first 4 digits are the abbreviation of the receiving bank, the 5th and 6th digits are the country code, and the 7th-11th digits are the regional identification code. For example, the SWIFT Code of Citibank Hong Kong Branch is CITIHKHX.
IBAN
IBAN refers to The International Bank Account Number (IBAN for short), which is a bank account number developed by the European Committee for Banking Standards (ECBS) according to its standards. The bank account numbers of member countries participating in ECBS all have a corresponding IBAN number, which is only applicable in Europe.
Encoding rules:
The numbering rules for IBAN include country code + bank code + region + account holder account number + verification code. The maximum number for IBAN is a 34-digit string.
Difference between IBAN and SWIFT Code:
Through the coding rules, it can be seen that the difference between IBAN and SWIFT Code is that IBAN can not only identify specific banks, but also the account number of specific bank account holders. SWIFT Code can only identify specific banks, but cannot identify specific account numbers within the bank.
When using IBAN, please note that IBAN is only applicable to Europe. If an IBAN account is not used in the Eurozone, an additional manual intervention fee will be charged.

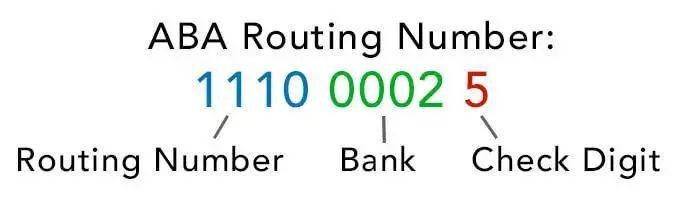
ABA Number
ABA Number, also known as Routing Number or Routing Transit Number, is a financial institution identification code proposed by ABA (US Bankers Association) under the supervision and assistance of the Federal Reserve.
Encoding rules:
The number consists of 9 digits (8 digits of content + 1 digit of verification code), mainly used in the US and North America. For example, the ABA number of US Bank of Hong Kong is 021508125. The Routing Number of the bank is usually printed in the lower left corner of the front of the US check.
ACH Number
ACH, the US Automated Clearing House, is a domestic remittance method with cheap fees. ACH Number is also a 9-digit code, usually the same as ABA Number, but specifically used for automated electronic transactions.
Purpose:
- Automated Clearing House (ACH): Mainly used to process electronic fund transfers such as payroll, supplier payments, and automatic bill payments.
- Electronic Transfer (EFT): including regular payments and one-time payments, usually processed through the ACH network.
Example:
123456789 (This is an example of the format of an ACH Number, which is usually consistent with an ABA Number)
Difference between ABA Number and ACH Number
Main differences:
- ABA Number: More widely used in various banking transactions, including paper checks and interbank transfers.
- ACH Number: Specifically for electronic payments and automated fund transfers.
Usage scenarios:
- ABA Number: Used for traditional banking transactions such as check processing and telegraphic transfer.
- ACH Number: Used for automated and electronic transactions such as direct deposit, bill payment and electronic funds transfer.
Conclusion:
Although ABA Number and ACH Number are often the same, their purposes are different. ABA Number is used to identify Financial Institutions for various banking transactions, while ACH Number focuses on electronic and automated transactions.
BSB Number
BSB Number, also known as Bank State Branch Number, is a telegraphic transfer clearing network code used in Australia and other places. It is a Unique Device Identifier for banks and other financial institutions in Australia. Providing BSB Number during remittance and transfer can accurately identify banks and other financial institutions to ensure that funds are accurately transferred to designated bank accounts.
Encoding rules:
The BSB Number consists of three parts, with a total of 6 digits. The first two digits represent the number of the state or territory where the Financial Institution is located, and the third digit represents the type of Financial Institution and its current location in the state or territory.
The first two digits can be any number from 01 to 99.
The third digit can be any number between 0 and 9.
The last three digits represent the specific branch of the Financial Institution.
Scope of application:
Mainly used in Australian and New Zealand dollar banks, as well as for clearing and settling payments to Australia. The scope of application is much smaller than SWIFT code.
Based on the above content, we can see that SWIFT CODE, IBAN, ABA, ACH, and BSB Number are all types of bank international telegraphic transfer codes, with only different usage regions. For example, countries and regions outside of North America and Europe mostly use SWIFT CODE, European banks (especially Germany) use IBAN, banks in the US and North America generally use ABA Number, and banks in Australia generally use BSB Number.
In fact, the function of SWIFT CODE is equivalent to the ABA Number in North America, but SWIFT CODE is more commonly used internationally. Generally speaking, there is no need for ABA Number and IBAN for remittances from Europe, because Chinese banks mainly use SWIFT CODE, so as long as you provide the SWIFT CODE of the receiving bank in China, it is enough.
If you want to telegraphic transfer money from China to an overseas region, you need to choose the corresponding telegraphic transfer code according to the location of the recipient’s bank. For example, if you want to transfer money to a US bank account through a bank in China, you only need to provide the ABA number of the US bank.
If you are transferring money to Europe, especially Germany, you only need to provide the IBAN code of the receiving bank. If you are transferring money to countries or regions outside North America or Europe, you only need to provide the SWIFT CODE of the receiving bank, because banks in these countries and regions generally use SWIFT CODE.
The benefits of using telegraphic transfer encoding are twofold: one is that telegraphic transfer funds arrive faster; the other is to save intermediate costs.
If there is no telegraphic transfer code, the payment may have to go through N transfers from the outgoing bank to the receiving bank. Each transfer requires a small fee to be deducted from the outgoing payment, usually $1-2. If there are 10 transfers, the amount received by the recipient will be reduced by about $20.
If there is telegraphic transfer encoding, it can reduce the transfer link and cost. Generally, only about 1-2 transfers are needed, so the cost generated by the intermediate link is only about 3-5 US dollars.
Therefore, if there is no detailed information and telegraphic transfer code of the other party’s bank, it is recommended to choose other remittance methods, such as bill transfer, etc.
How to check the bank’s SWIFT Code?
If you want to check your bank’s SWITF Code, you can usually find your bank’s SWIFT/BIC code in the bank statement, or you can directly call or ask the bank staff. Of course, you can also search by bank or country/region on BiyaPay’s official website to obtain the correct SWIFT CODE. If you already have your bank’s international code, you can also use its checker to verify it.
SWIFT bank code is used to help banks process remittances from overseas. If you want to make international remittances or receive payments between banks, especially international telegraphic transfers or SEPA transfers, in addition to the required SWIFT code, you also need to choose a suitable remittance tool.
You can use the global multi-asset trading wallet BiyaPay for overseas remittances, which not only simplifies the remittance process, but also ensures the security of funds and the convenience of transactions.
Its functions include global payment and international remittance, as well as major investment services such as US/Hong Kong stocks, options, and digital currencies. It supports real-time exchange rate queries and exchanges for more than 20 legal currencies and more than 200 digital currencies, allowing for local remittances in most countries or regions around the world anytime, anywhere, with fast arrival speed, low handling fees, and unlimited limit.
Moreover, BiyaPay provides competitive exchange rates to reduce remittance costs, with low procedure fees and no other hidden fees. It has obtained financial licenses such as the US, Canada, US SEC, and New Zealand, making your digital currency to fiat currency exchange safer and more legal, avoiding the risk of being frozen over the counter. With complete KYC certification and professional and legal offshore accounts, every remittance is taken seriously, allowing users to transfer every penny with peace of mind. This greatly improves the efficiency and security of international remittances, making cross-border fund flows smoother.